Early blight, late blight, and leaf spot are common fungal diseases of tomato plants.
Late blight is the most serious of the three. It spreads rapidly and will likely destroy the infected plant and can quickly spread to other plants—including potatoes, eggplants, and peppers.
Here are the basics for identifying these fungal diseases:
Conditions for disease growth
- Early blight: high humidity; temperatures above 75°F; transmission hastened by wind, heavy dew, and frequent rain; poor plant nutrition contributes.
- Late blight: high humidity; temperatures between 60° and 80°F; wind-, rain-, and soil-borne. Infection often occurs before blossoming. Spores germinate readily at about 70°F. Watch for disease when cool, moist nights are followed by warm, muggy days.
- Leaf spot: high humidity; temperatures between 60° and 80°F.
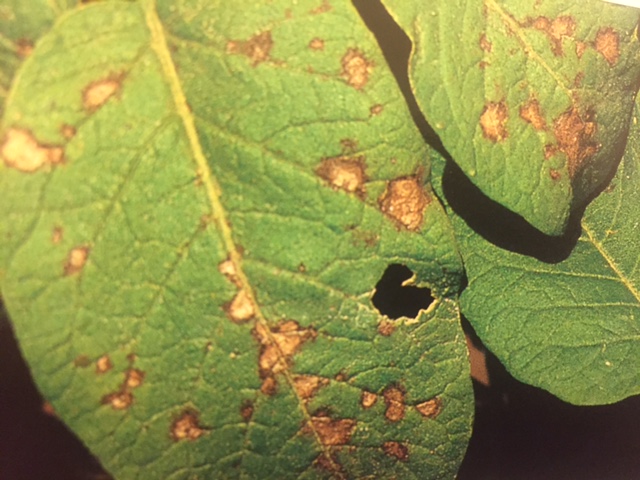
Leaf symptoms
Early blight
Symptoms appear first on older, mature leaves near the base of the plant–one or two spots per leaf, spots ¼ to ½ inch in diameter; spots have tan centers with concentric rings and yellow halos around the edges, target-shape appearance with defined border; spots enlarge and coalesce. A large portion of the leaf becomes a diffuse yellow and may drop. No mold appears. The disease spreads slowly.
Late blight
Water-soaked spots show first on lower leaves; spots start out pale green diffuse irregular spots on the upper side of the leaf, usually near the edges of tips of leaves; spots turn brown to purplish-black and velvety with a pale green border on the underside of the leaf; spots appear on young leaves at the top of the plant; spots look water-soaked; no concentric rings or defined border around necrotic spots. In humid, wet conditions, a fuzzy ring of mold around the spot appears on the undersides of the leaves. Leaves shrivel, turn brown, and die. The disease spreads rapidly.
Leaf spot
Numerous brown spots appear on the leaves 1/16 to 1/4 inch in diameter; spots are circular with dark brown margins and tan to gray center–a black speck in the center; spots do not have a yellow halo. The disease spreads upwards from oldest to youngest. Leaves turn slightly yellow, then brown, then wither.
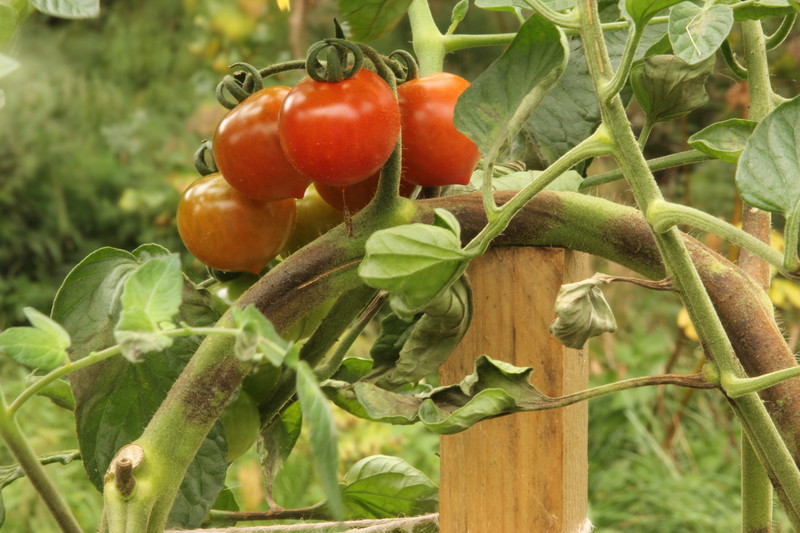

Stem symptoms
Early blight
Dark, sunken lesions appear on the stem at or above the soil line, sometimes called collar rot.
Late blight
Black and brown lesions appear on the stem and petioles; when petioles or leaf stalks are affected, the entire leaf can collapse; the entire vine or plant can quickly collapse and die in periods of high humidity.
Leaf spot
There is no stem damage.
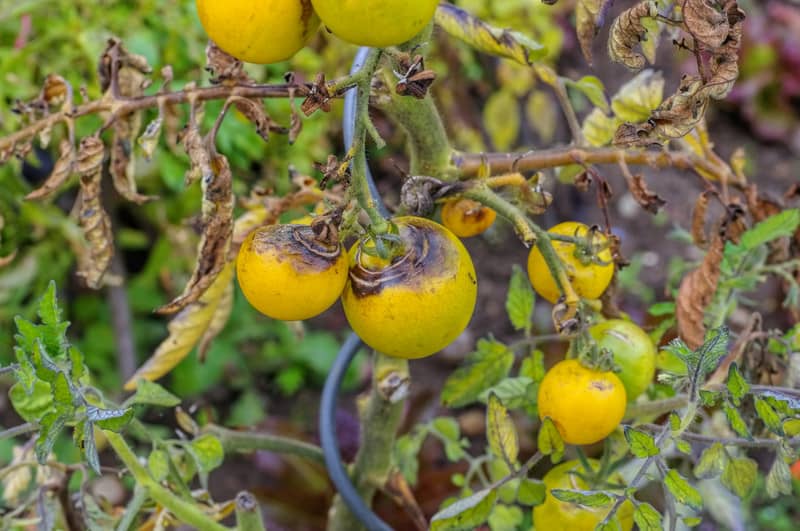

Fruit symptoms
Early blight
Sunken spots appear on the stem end of fruits; concentric ring pattern or target-shape appearance around spots; disease moves from stem to rot fruit.
Late blight
Spots beneath the skin develop on tops and upper sides of green fruit; spots become reddish-brown, firm, dry, and leathery; spots grow larger; the skin wrinkles and darkens to chocolate brown; soft rot sets in; white mold forms in damp, humid conditions.
Leaf spot
Fruit is usually not affected; sunscald may occur as a result of leaf loss above.
Treatment of disease
Early blight
Remove lower leaves after first fruit sets; then remove affected leaves as they appear; plant in a different location next year.
Late blight
Pull and destroy the plant as soon as you know its late blight; select resistant varieties to plant in the future; plant in a different location next year.
Leaf spot
Remove infected leaves as they appear; improve air circulation around plants; clean tools after use; clean plant stakes and cages; plant in a different location next year.
Prevention of fungal diseases
- Remove diseased leaves as soon as they appear.
- Improve air circulation around plants.
- Mulch around the base of plants to reduce water splashing.
- Do not use overhead watering.
- Control weeds.
- Rotate crops.
Scientific name of diseases
- Early blight, Alternaria solani
- Late blight, Phytophthora infestans
- Leaf spot, Septoria lycopersici
In-depth articles on these diseases:
Related articles:
Vegetable Garden Diseases Problem Solver
Vegetable Garden Organic Weed Control
Vegetable Garden Organic Pest Control
Garden Planning Books at Amazon:
- Vegetable Garden Almanac & Planner
- Kitchen Garden Grower’s Guide Vegetable Encyclopedia
- Vegetable Garden Grower’s Guide
- Tomato Grower’s Answer Book
Tomato articles at Harvest to Table:
How to Plant and Grow Tomatoes
How to Choose a Tomato for Your Garden
Growing Tomatoes in Containers
Growing Early Season Tomatoes for Great Taste
Epsom Salt, Milk, and Organic Fertilizers for Tomatoes and Peppers
How to Prevent Blossom Drop – Tomatoes and Peppers
How to Harvest and Store Tomatoes
Nine Ways to Cook and Serve Tomatoes
Tomato Sauce–Basic, Herbed, or Vegetables Added
How to Make Tomato Juice Simply
How to Home Can Tomatoes for Beginners
How to Sun Dry and Oven Dry Tomatoes
Tomato Growing Problems Troubleshooting
How to Prevent Tomato Blossom Drop
How to Identify Early Blight, Late Blight, and Leaf Spot
Tomato Hornworm Organic Pest Control















