Septoria leaf spot is a fungal disease. It is one of the most destructive tomato plant diseases and affects a wide range of other vegetables and garden plants as well.
Septoria fungal leaf spot is most severe in regions where warm, wet, humid weather extends over several days to weeks.
Disease range: Throughout North America
Scientific name: Septoria spp.; Septoria lycopersici (tomatoes); Septoria apiicola (celery)
Good Products for Pest and Disease Control at Amazon:
- Garden Safe Snail and Slug Bait
- Bonide Sulfur Fungicide
- Monterey BT Caterpillar Killer
- Neem Bliss 100-% Cold Pressed Neem Oil
- Safer Brand Insect Killing Soap
- PyGanic Botanical Insecticide
Septoria leaf spot target plants
Septoria leaf spot attacks tomato, celery, and cucumber-family crops.
Septoria leaf spot: conditions for disease growth
Septoria leaf spot occurs during periods of high humidity when temperatures are between 60° and 80°F.
Septoria leaf spot damage
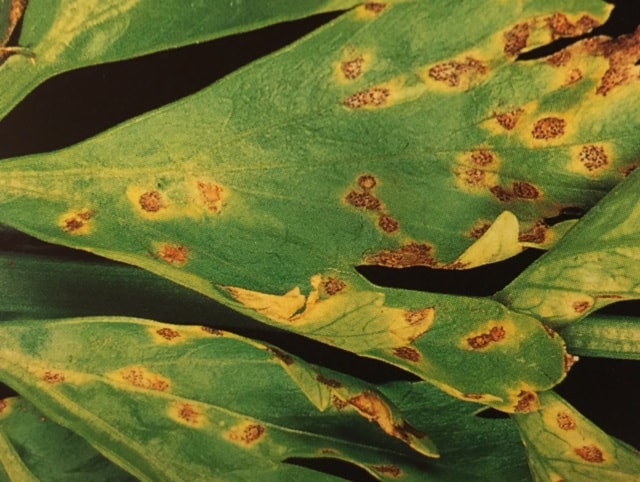
Leaf damage starts as small yellow spots that gradually turn brown; spots are 1/16 to 1/4 inch in diameter; spots become circular with dark brown margins and tan to gray center–a black speck in the center (black pycnidia, which are fungal fruiting bodies); spots may or may not have a yellow halo. The disease spreads upwards from oldest to youngest. Leaves turn slightly yellow, then brown, then wither and die and drop.
Stem and fruits are not usually affected, but sunscald to fruits below leaves affected may occur as diseased leaves drop.
How Septoria leaf spot spreads
Septoria fungi spores are wind- and rain-borne. Hyphae enters the plant through cracks and wounds in plant tissue.
Septoria leaf spot life cycle
Fungi overwinter on decomposed plant debris and form new spores each spring. Several generations of spores can occur during summer when the disease is widespread.
Septoria leaf spot organic control and prevention
- Remove and destroy infected leaves as they appear; check lower and inner leaves often for signs of the disease.
- Improve air circulation around plants; stake or trellis plants.
- Do not use overhead irrigation.
- Mulch around the base of plants to stem water splash which can contain fungi spores.
- Clean tools after use; clean plant stakes and cages; plant in a different location next year.
- Clean the garden of plant debris at the end of the season; fungi can overwinter in weeds and debris.
- Remove weeds from the garden particularly nightshade family weeds which can harbor fungi spores.
- Use disease-free seed.
- Treat self-saved tomato seeds with a 122°F hot water bath for 20 minutes.
- Foliar spray plants with compost tea.
- Rotate crops—do not plant tomato family crops in the same spot more often than every three years; plant resistant cultivars.
Septoria leaf spot non-organic treatment
- Fungicides do not cure Septoria leaf spot but they can help prevent it or stem the spread. Apply chlorothalonil, maneb, macozed, or copper-based fungicides such as copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture at 7 to 10-day intervals.
General prevention of fungal diseases
- Remove diseased leave as soon as they appear.
- Improve air circulation around plants.
- Mulch around the base of plants to reduce water splashing.
- Do not use overhead watering.
- Control weeds.
- Rotate crops.
Related articles:
Vegetable Garden Diseases Problem Solver
Vegetable Garden Organic Weed Control
Vegetable Garden Organic Pest Control
Garden Planning Books at Amazon:
- Vegetable Garden Almanac & Planner
- Kitchen Garden Grower’s Guide Vegetable Encyclopedia
- Vegetable Garden Grower’s Guide
- Tomato Grower’s Answer Book















