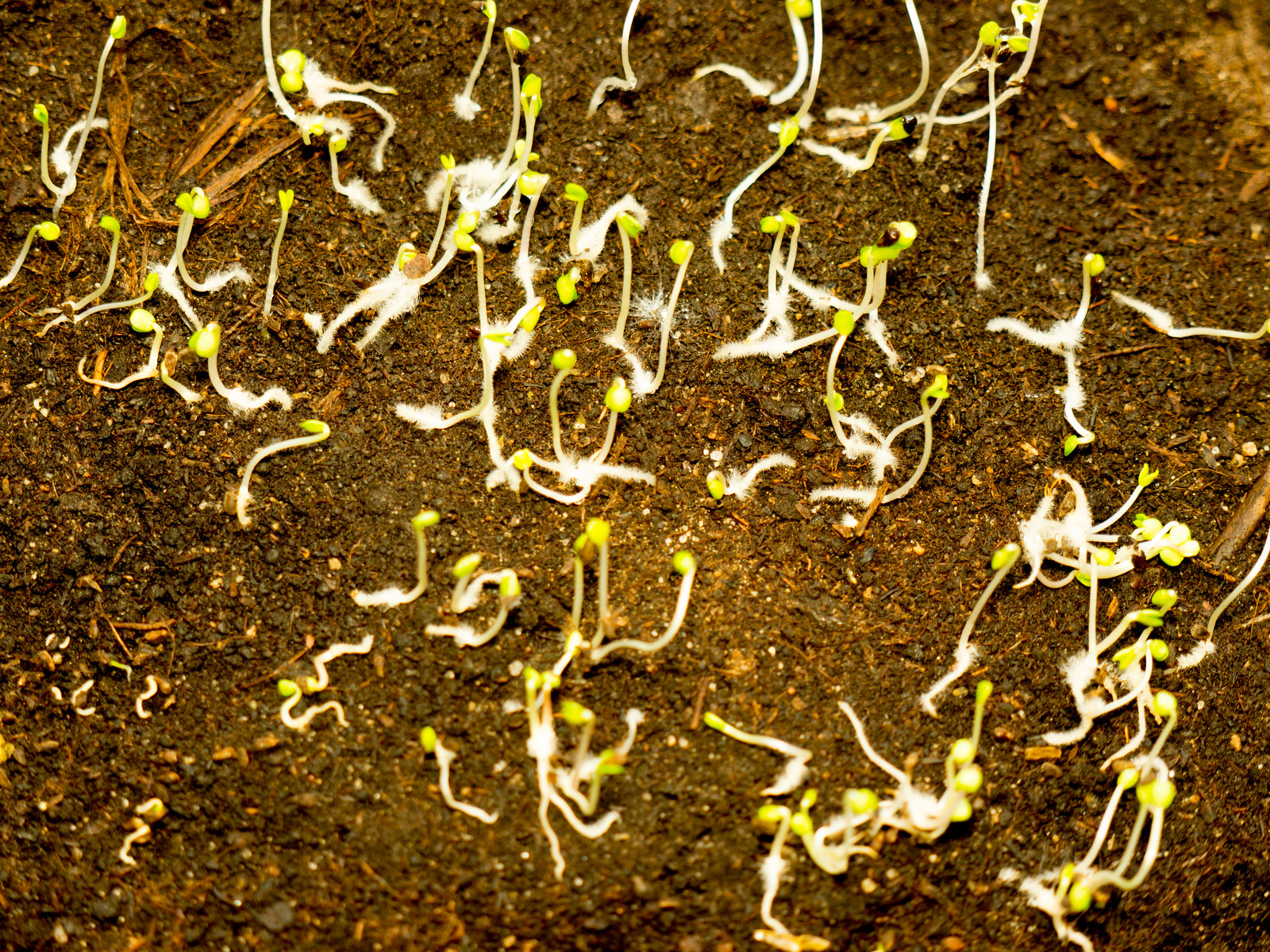
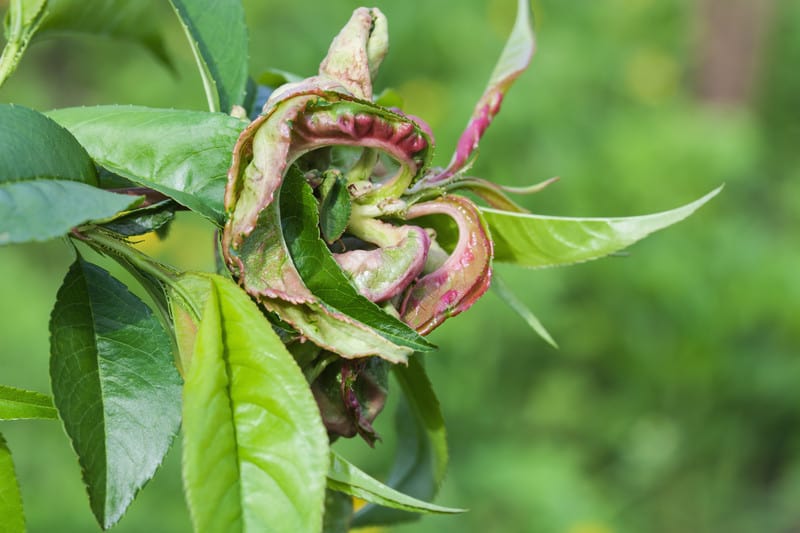
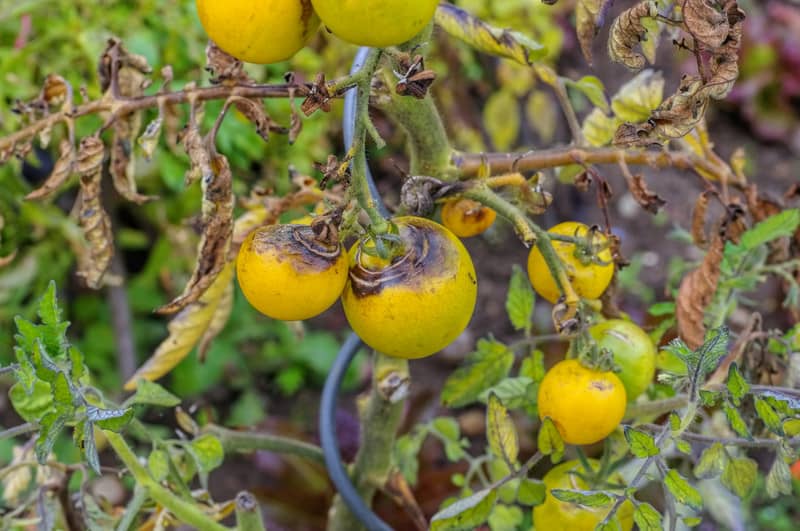
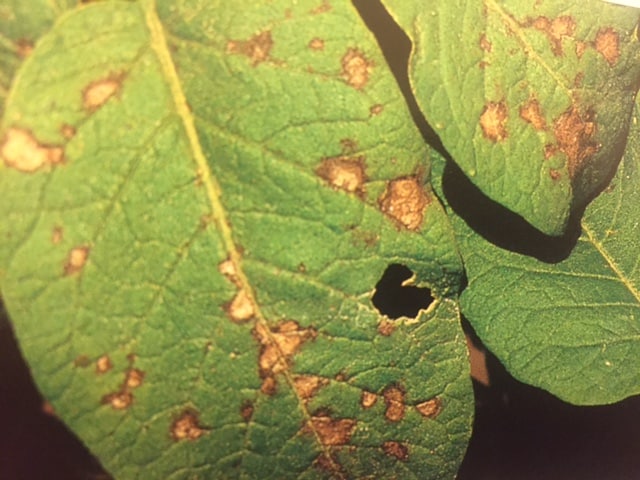
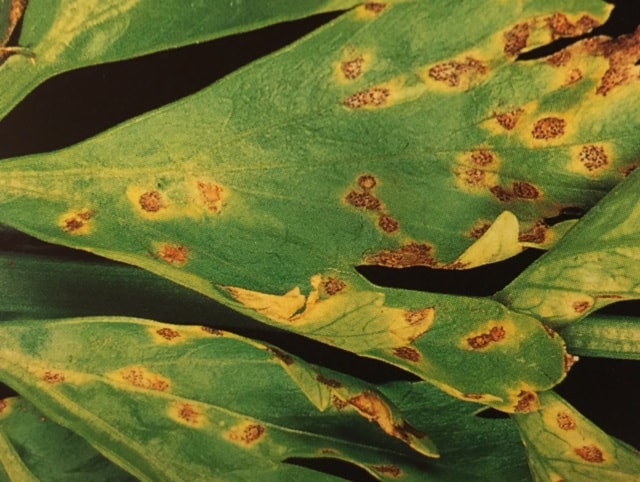
Vegetable Garden Diseases Problem Solver
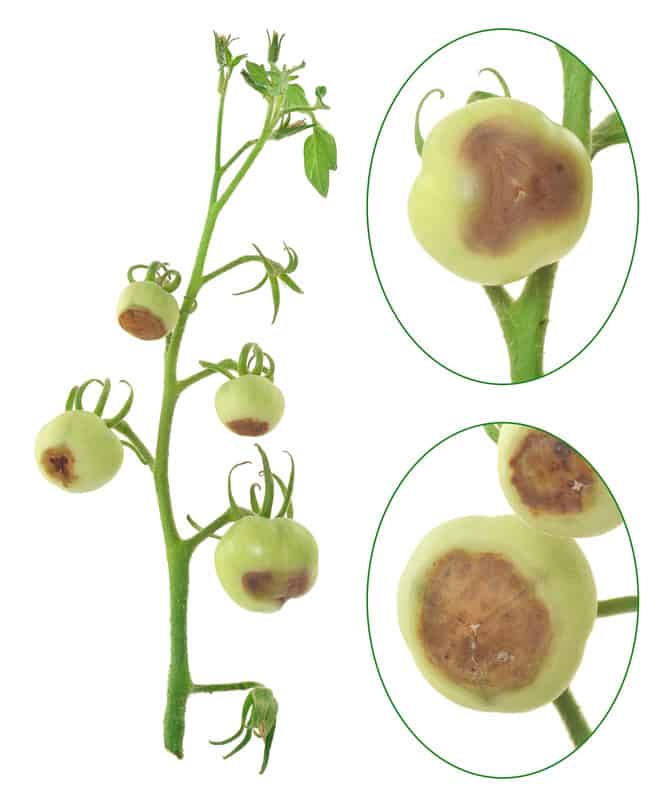
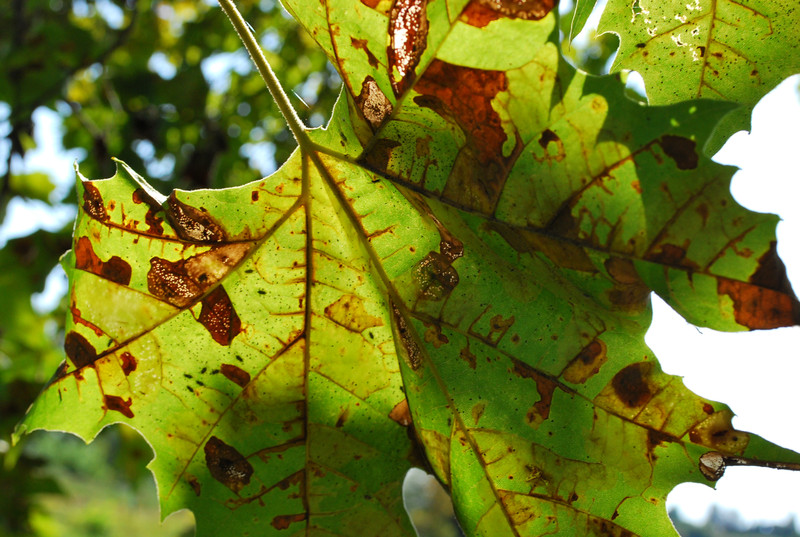
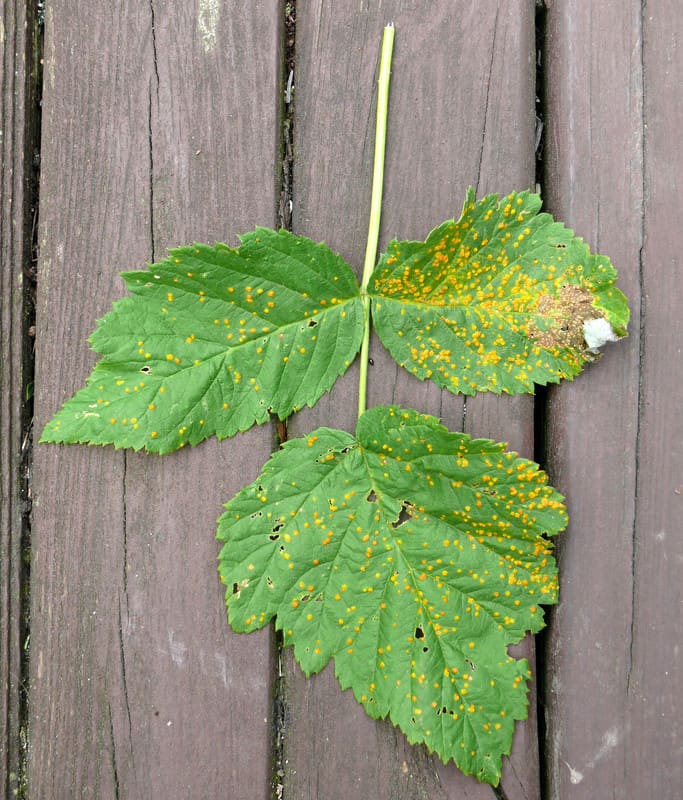
Most vegetable garden diseases can be prevented and controlled. Limit disease damage by identifying diseases quickly and taking action. Regular visits to the garden will help you spot diseased plants before the disease spreads. Choose the most effective control and then work to prevent future disease outbreaks. Listed here are 25 common vegetable diseases. The […] More