Raised Bed Buyer’s Guide
Raised beds are popular among gardeners for good reason. These elevated gardening systems offer a host of benefits, making them a great choice for both novice and experienced gardeners alike. With their ability to improve drainage, soil structure, and accessibility, raised beds provide an ideal environment for growing vegetables, herbs, flowers, and even small shrubs.
In this buyer guide, we will explore the various aspects of raised beds to help you make an informed decision when selecting the right one for your gardening needs. Whether you have limited space, poor soil quality, physical limitations, or simply want to enhance the aesthetics of your garden, raised beds can be an excellent solution.
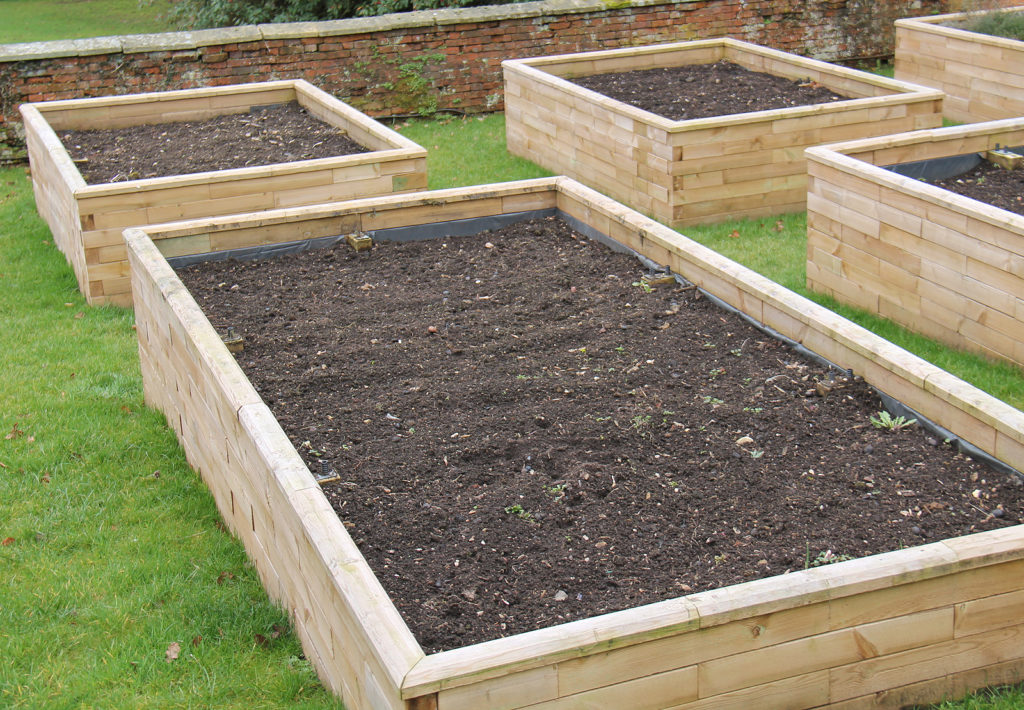

Raised bed benefits
Raised beds are typically made of wood, metal, recycled plastic, or concrete, or stone. Here are some compelling reasons to invest in raised beds:
Defined space
Raised beds provide a defined space for gardening. This is particularly useful if you have limited garden space or an unconventional yard layout. By confining your garden to raised beds, you can maximize the use of available space and prevent the encroachment of weeds or grass. Additionally, the defined boundaries make it easier to maintain and organize your plants, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of your garden.
Control of soil
Raised beds allow the gardener to control soil conditions. By using a mixture of high-quality soil, compost, and other organic materials, you can create a nutrient-rich environment that fosters healthy plant growth. This is particularly beneficial if you are dealing with heavy clay or sandy soil, which can impede proper root development. Additionally, raised beds are less prone to soil compaction, allowing better water drainage and reducing the risk of waterlogged roots.
Accessibility
Raised bed height can make gardening more accessible and convenient. If you have physical limitations or find it challenging to bend or kneel for extended periods, waist-high raised beds offer a solution. The raised height reduces strain on your back as you can garden at a comfortable height, making it easier to plant, weed, and harvest. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for older gardeners or those with limited mobility.
Water drainage and retention
Raised beds help with water drainage and retention. Raised beds typically have open bottoms and well-drained soil, which prevents waterlogging and allows excess water to flow away, preventing root rot and other water-related issues. Raised beds also help retain moisture in the soil, reducing the need for frequent watering. This efficient water management system not only saves you time and effort but also promotes healthier plants by avoiding over or under-watering.
Weed and pest control
Raised beds offer greater control over pests and weeds. By providing a defined area for your plants, you can effectively manage unwanted intruders. Installing a barrier at the base of the bed can prevent burrowing animals, such as gophers or moles, from harming your plants. Additionally, with less space for weeds to spread, raised beds require less maintenance and weeding, making gardening more enjoyable and efficient.
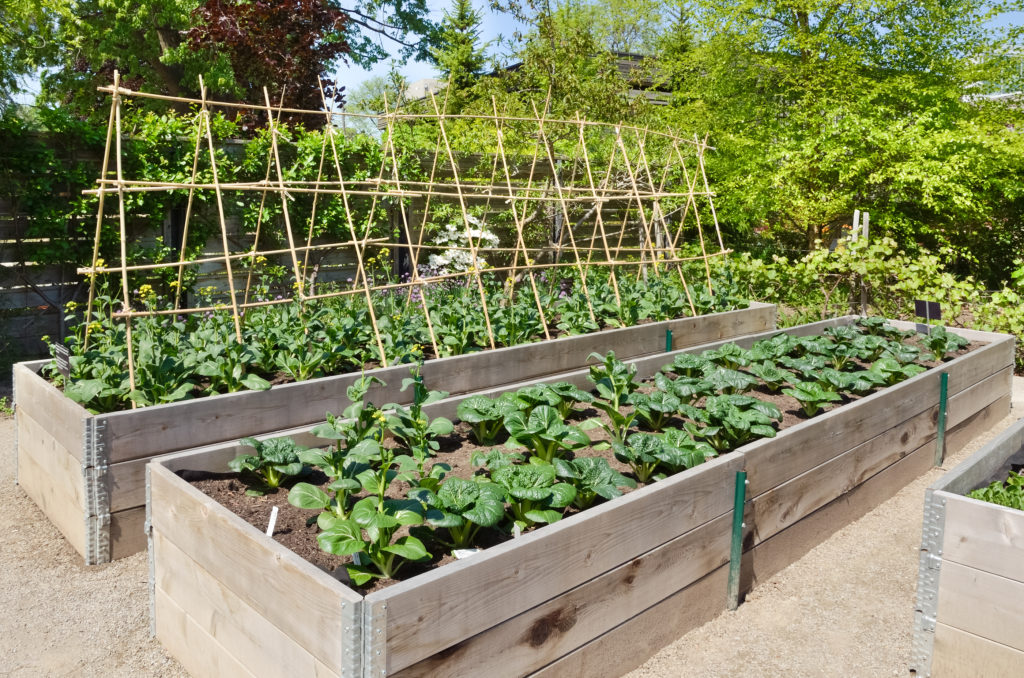

Materials for raised beds
Raised beds can be made of different types of materials. Here are common materials used for raised beds:
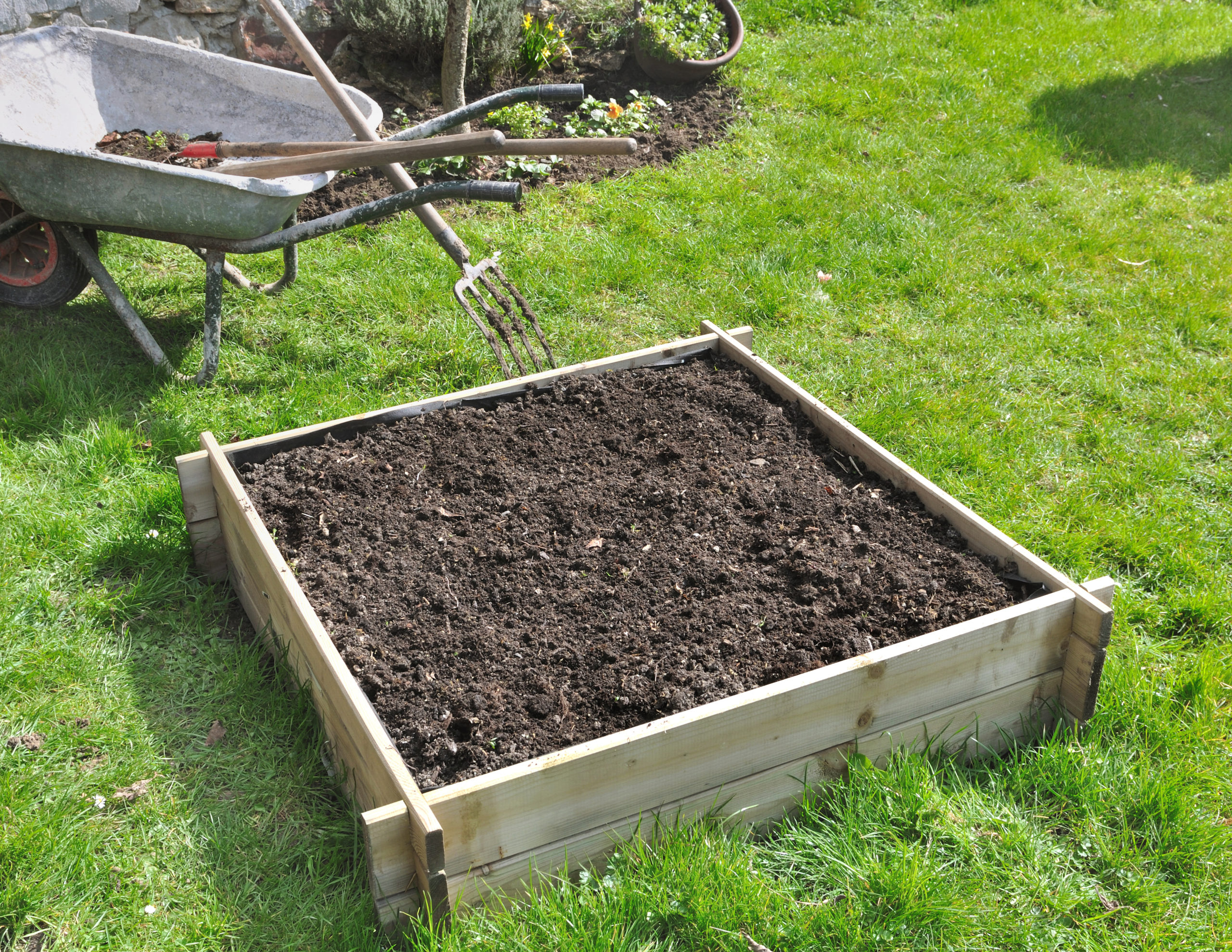
Wooden raised beds
Wooden raised beds are typically made from rot-resistant lumber such as cedar or redwood, ensuring durability and longevity. The wooden frames can be customized to various sizes and heights, which is ideal for accommodating specific plants’ needs or making it easier for individuals with mobility issues. Wooden raised beds offer a natural look to any garden. It is important to choose wood that has not been chemically treated for a raised bed.
Metal raised beds
Metal raised beds are usually made from galvanized steel or aluminum, making them resistant to rust and corrosion. Metal raised beds are known for their sturdiness and ability to withstand extreme weather conditions. Additionally, metal beds often come in a variety of colors and finish options, allowing you to add a touch of style to your garden. Metal raised beds offer a modern and sleek appearance.
Recycled plastic raised beds
Recycled plastic raised beds are made from post-consumer recycled materials, these beds are not only durable but also contribute to reducing environmental waste. They are lightweight, easy to assemble, and resistant to rot and decay. Recycled plastic raised beds are perfect for gardeners who prefer a eco-friently, low-maintenance option that can endure the test of time.
Concrete block raised beds
Concrete block raised beds offer a sturdy and permanent solution for raised beds. The blocks are stacked to create a raised structure, which can be filled with soil. Concrete blocks provide excellent heat retention and are ideal for areas with cooler climates. Concrete blocks can be stacked to create higher beds, allowing for deep-rooted plants or individuals with mobility concerns. They not only provide a stable base for plants but also serve as a practical edging solution for garden borders. Some gardeners prefer the more modern appearance and durability that concrete blocks provide.

Types of raised beds
There are several types of raised beds to consider. Each type has its own benefits and features that make them unique. From waist-high beds to hugelkultur beds, here are a few popular types of raised beds that you can incorporate into your gardening space.
Waist-high rasied beds
As the name suggests, waist-high beds are elevated garden beds that are designed to be at the perfect height for gardening without bending or crouching. These beds are ideal for individuals with mobility issues or those who prefer to garden without straining their backs. They provide excellent drainage and are easy to access, making them a popular choice for many gardeners.
Hugelkultur rasied beds
Hugelkultur rasied beds are a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for raised bed gardening. This type of bed uses logs and branches as the base layer, followed by compost, soil, and mulch. As the organic materials break down, they release nutrients into the soil and provide long-lasting fertility. Hugelkultur beds also enhance water retention, making them perfect for dry climates or areas with inconsistent rainfall.
Keyhole and U-shaped raised beds
Keyhole and U-shaped raised beds are a clever design that maximizes growing space while minimizing the need for extensive maintenance. These beds are shaped like a keyhole or U, with an opening that allows easy access to the entire bed. Keyhole and U-shaped beds are perfect for small gardens and are especially popular in permaculture systems. With their near-circular design, they promote efficient use of space and are aesthetically pleasing.
Square foot gardens raised beds
Square foot gardening is a technique that involves dividing the raised bed into small 1×1-foot sections. Each section is then planted with a specific crop according to its space requirements. This method reduces the need for excessive weeding and creates a neat and organized garden layout. Square foot gardens are perfect for small spaces, and they make it easy to manage and rotate crops efficiently.
Container raised beds
If you have limited space or are gardening on a balcony or patio, container beds are an excellent choice. These portable raised beds are created using containers such as pots, wooden crates, or beds on wheels. They give you the freedom to move your garden around and experiment with different layouts. Container beds are perfect for growing herbs, vegetables, and flowers, providing a compact and versatile solution for urban gardeners.
Raised bed selection tips
Raised beds have become increasingly popular due to their numerous advantages. They offer better control over soil quality, drainage, and temperature, making them the preferred choice for both seasoned gardeners and beginners alike. However, selecting the right size raised bed is crucial for the success of your garden. Here are a few things to consider when determining the size of your raised bed.
Firstly, think about the available space in your garden. Measure the area where you plan to place the raised bed and take note of any obstructions such as trees or buildings. It is important to ensure that there is enough room for you to comfortably move around the bed for maintenance and harvesting. Additionally, consider the amount of sunlight the area receives as this will play a role in determining what you can grow.
Next, think about the types of plants you intend to grow and their spacing requirements. Some plants, such as tomatoes or pumpkins, require more space to spread out, while others, like lettuce or herbs, can be planted closer together. Research the recommended spacing for your desired plants and factor this into your raised bed size decision.
Consider your gardening goals and the amount of time and effort you can dedicate to maintenance. If you have a busy schedule or limited physical abilities, a smaller raised bed may be more manageable. On the other hand, if you have ample time and enjoy spending it in the garden, a larger bed may be more suitable to accommodate a wider variety of plants.
Lastly, think about the depth of the raised bed. Different plants require different depths of soil for their roots to thrive. While most vegetables can grow in a bed with a depth of around 6 to 12 inches, root crops like carrots or potatoes may require deeper beds. Take into account the specific requirements of the plants you wish to grow and choose a raised bed that meets those needs.
Selecting the right size raised bed is essential for a successful and productive garden. Consider the available space, types of plants, gardening goals, and required depth of soil to determine the appropriate size for your raised bed. With careful planning, you can create a thriving garden that yields a bountiful harvest.

Where to place a raised beds
Choosing the right location for your raised bed is crucial for the success of your gardening efforts. Before situating your raised beds, take some time to consider the following factors and find the perfect spot for your raised bed.
Sunlight
Sunlight is one of the most important factors to consider. Most vegetables and flowers require at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Therefore, choose a location that receives ample sunlight throughout the day. Avoid planting your raised bed in areas shaded by trees or buildings, as this will hinder plant growth and limit your gardening outcomes.
Accessibility
Accessibility of your raised bed is important. It should be placed in an area that is easily accessible for regular maintenance and harvesting. Assess the distance from your house, water sources, and storage areas. Having your raised bed in close proximity to these amenities will make your gardening experience more convenient and enjoyable.
Soil
Depending upon the height of the raised bed, the soil beneath the bed can be important. Low-risie raised beds may require improvement of the soil beneath them. Before choosing a location, perform a soil test to determine its quality and fertility. Ideally, your raised bed should be placed on well-draining soil with a pH level suitable for the plants you wish to grow. Taking the time to amend the soil before setting up your raised bed will greatly benefit your plants and yield healthier produce.
Surrounding environment
Consider the environment that will surround your raised bed. Look for a spot that is sheltered from strong winds or excessive exposure to extreme weather conditions. This will protect your plants from damage and ensure their optimal growth. Also, consider any neighboring plants or structures that may cast unwanted shade on your raised bed.
Aesthetics
Considere aesthetics when siting raised beds. Your raised bed should enhance the overall beauty of your garden. Choose a location that complements the existing landscape and creates a visually appealing focal point.
More Buyer’s Guides