Parasitic Wasps Beneficial Insects
Parasitic wasps are small, even minute, mini-wasps that control pests including many garden pests.
Parasitic wasps kill their hosts by feeding on them. Pests controlled by parasitic wasps include aphids, beetles, caterpillars, flies, sawflies, and scale insects.
Notable parasitic wasps are the Braconid wasp, the Chalcid wasp, the Ichneumon wasp, and the Trichogramma wasp.
Parasitic wasps range in size from 1/100 to ¾ inch long. They vary in shape and coloration but have a notable narrow “waist” between the thorax and abdomen and long thread-like antennae. The larval stages usually do the most damage to pest insects developing inside or outside the hosts and then chewing the host for food. This is called “host feeding” and reduces the population of host pest insects.
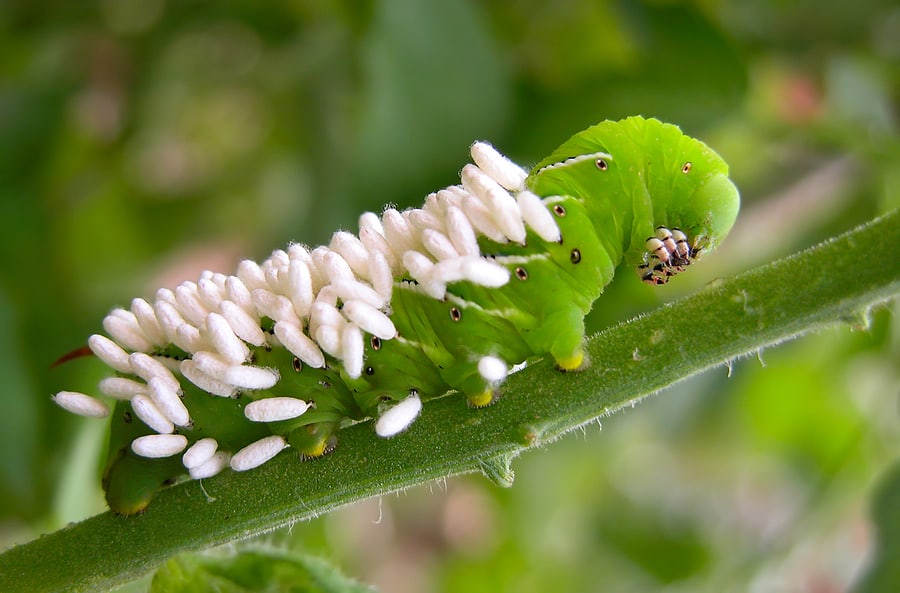
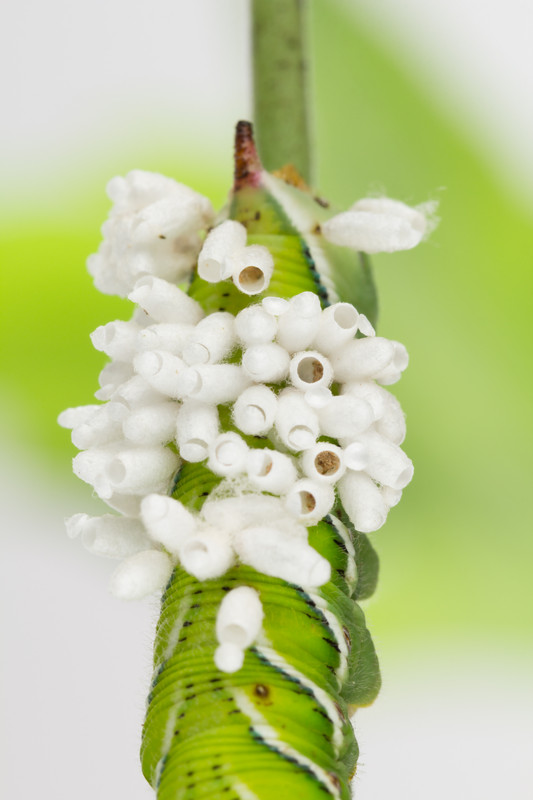
Parasitic wasps are noticeably seen victimizing tomato hornworms; their egg-like white cocoons are seen traveling on the backs of hornworms—the host has already been parasitized by the wasp larvae and is near death or will not be able to pupate.

Notable parasitic wasp families
Parasitic wasps belong to the order Hymenoptera. Here are notable members of that family:
Braconid wasps
Braconid wasps feed on aphids, garden webworms, tomato hornworms, armyworms, strawberry leaf rollers, and tent caterpillars; they are just 1/16 to 5/16 inch long and brown or red-bodied.
Chalcid wasps including the Trichogramma wasp
Chalcid wasps include the Trrichogramma wasp. These wasps feed on moth and butterfly larvae, including cabbage worms, tomato hornworms, corn earworms, cutworms, armyworms, webworms, cabbage loopers, and corn borers, and also aphids and mealybugs. The Trichogramma wasp is an important parasite of codling moth eggs. These wasps are 1/64 to 5/16 inch long and metallic black or golden bodied.
Ichneumon wasps
Ichneumon wasps feed on cutworms, corn earworms, white grubs, and caterpillars. These wasps are ⅛ to 1½ inches long.

More about Braconid beneficial wasps
The Braconid wasp is one of the most important and common parasitic wasps
Braconid wasps belong to the Family Braconidae. There are between 50,000 and 150,000 species of Braconi wasps worldwide including in North America
Adult Braconid wasps are black, yellowish, or red; 1/10 to ¼ inch long with narrow, threadlike waists. Braconid larvae are white to cream-colored, and wormlike.
Braconid wasp life cycle
There are several generations of Braconid wasps each year. Most species hibernate as larvae or pupae in their hosts. Females inject eggs into host insects including grubs and caterpillars. Larvae hatch and grow inside the host insect, weakening and often killing it, or the adult wasp paralyzes the host insect before laying the eggs. The larvae pupate on the back of the host
Braconid wasp feeding habits
Adult Braconid wasps feed on the pollen and nectar of small flowers including dill, parsley, and yarrow. The larvae feed inside caterpillars, beetle grubs, and aphids. Adults also feed on aphids, codling moths, cucumber beetles, cutworms, gypsy moths, imported cabbage worms, tent caterpillars, and tomato hornworms.
Good Products for Pest and Disease Control at Amazon:
- Garden Safe Snail and Slug Bait
- Bonide Sulfur Fungicide
- Monterey BT Caterpillar Killer
- Neem Bliss 100-% Cold Pressed Neem Oil
- Safer Brand Insect Killing Soap
- PyGanic Botanical Insecticide
How to attract parasitic wasps
Parasitic wasps are attracted to the garden by an ample supply of water—a shallow birdbath or garden pond will do, and a good supply of nectar—plant alyssum, dill, cilantro, parsley, and yarrow–and host insects to feed on.
Related articles:
Vegetable Garden Beneficial Insects
Vegetable Garden Organic Pest Control
Vegetable Garden Diseases Problem Solver
Vegetable Garden Organic Weed Control
Garden Planning Books at Amazon: